Risk management is the backbone of successful stock and cryptocurrency trading. Amidst the turbulence of the financial markets, it's not merely the strategy or technical skills that secure longevity - it’s the trader’s ability to manage risk intelligently and responsibly. This article is a transformative exploration of effective risk management strategies, inspired by advanced trading principles. By the end, you'll gain a deep understanding of the interplay between risk, psychology, and behavior, along with actionable techniques to elevate your trading game.
Understanding Risk in Trading: A Foundational Perspective
The Nature of Risk and Uncertainty
At its core, risk stems from uncertainty - the inability to predict outcomes with absolute certainty. Unlike general uncertainty, risk is measurable: it’s the quantified potential for loss you accept when placing a trade. While it’s impossible to eliminate uncertainty, well-implemented risk management neutralizes its dangers, enabling traders to survive - and eventually thrive - in volatile markets.
The key takeaway? You can’t control whether your next trade will win or lose, but you can control how much you're willing to lose if things go wrong. This principle forms the bedrock of sustainable trading practices.
The Three Pillars of Trading Success
Successful trading lies at the intersection of technique, psychology, and risk management, often referred to as the "trading tripod." Here’s how each component interrelates:
-
Trading Technique: A sound strategy builds confidence and reduces hesitation, but even the best strategies are never foolproof.
-
Trading Psychology: Emotional biases, cognitive pressures, and stress can derail execution - even when the trader knows the right moves to make.
-
Risk Management: This is the most controllable element of the triad. Effective risk management mitigates the flaws of both technique and psychology, allowing traders to survive losing streaks and capitalize on winning runs.
The Cost of Neglecting Risk Management
Many traders fall into the trap of endlessly tweaking strategies to optimize results, believing their losses stem from technical inefficiencies. In reality, poor risk management - not an imperfect strategy - is often the root cause of failure. While strategies can win or lose in isolation, only solid risk management ensures long-term survival and growth.
Core Challenges of Risk Management
Challenge 1: Balancing Stop-Losses and Profit Targets
A primary challenge for traders is minimizing stop-loss sizes to reduce capital risk while avoiding premature exits. Similarly, traders struggle to maximize profit targets without leaving gains on the table. Success lies in striking the right balance to achieve optimal growth while staying protected from market noise.
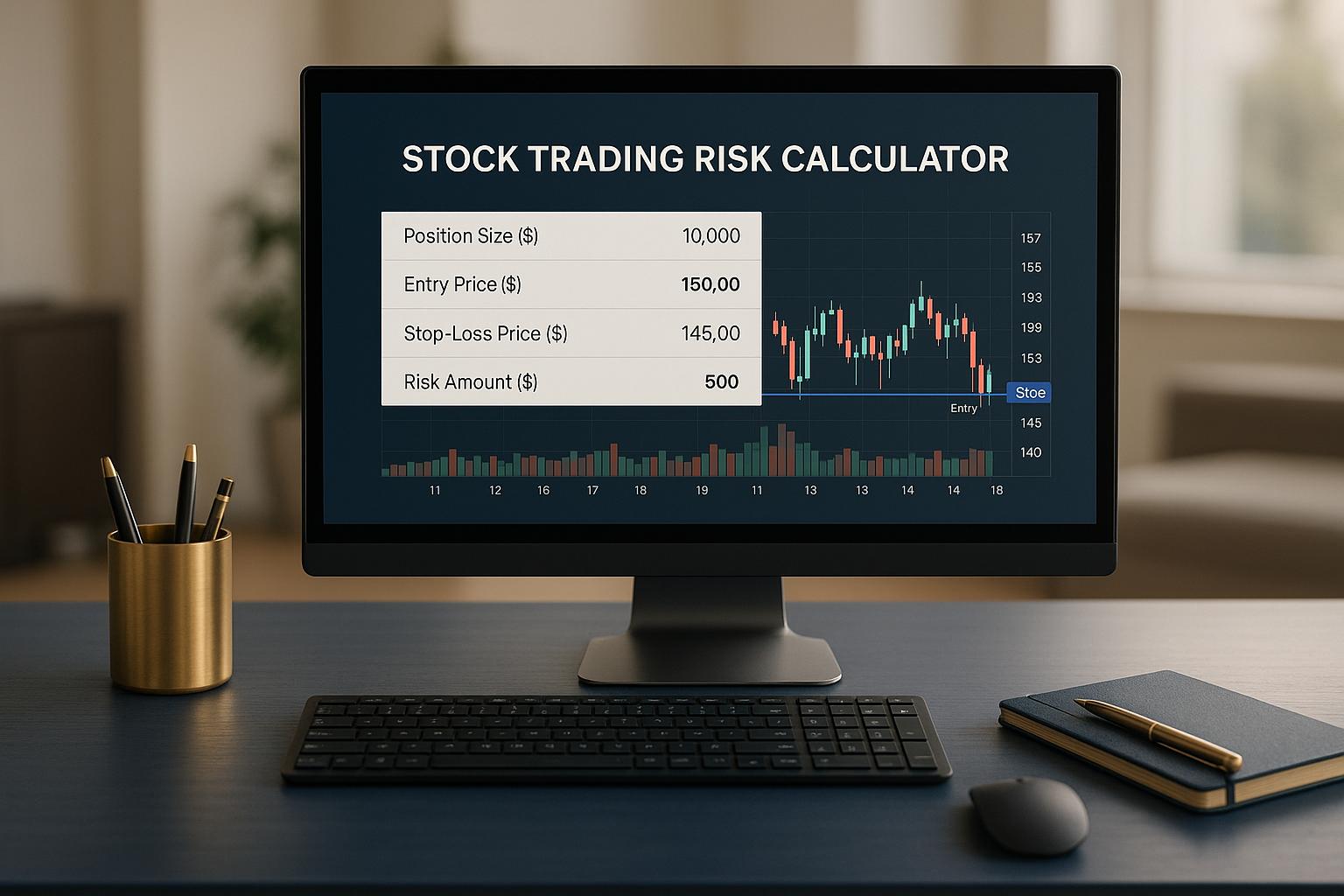
Challenge 2: Determining the Right Position Size
Position sizing is critical. Traders must decide how much capital to risk per trade to maximize account growth while avoiding exposure to ruinous losses. This calculation requires careful consideration of account size, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Analogies to Simplify Risk Management
The Ship in a Storm
Imagine facing a storm in two possible vessels: a large, steady ship designed for endurance or a small, fast boat that’s vulnerable to capsizing. The large ship represents the disciplined trader who prioritizes sustainability, while the small boat mirrors the overleveraged speculator chasing short-term thrills. Trading isn’t about speed - it’s about survival. Long-term success belongs to those who prioritize consistency over intensity.
The Minefield
Crossing a minefield symbolizes navigating market risks. While it’s impossible to predict every mine’s location (akin to technical analysis), you can reduce risk by walking cautiously, shortening paths, and wearing protective gear. Similarly, traders should focus on smart risk management rather than attempting to predict every market move with precision.
Advanced Concepts in Risk Management
The Asymmetry of Wins and Losses
Losses and gains are not symmetrical. For example, a 10% loss requires an 11.1% gain just to break even. As losses deepen, recovery becomes exponentially harder: a 50% loss demands a 100% rebound, while a 90% drawdown requires a staggering 900% recovery. This underscores the importance of protecting capital at all costs.
The Illusion of Consistency
Many traders aspire to achieve consistent profitability, mistaking it for an endless sequence of winning trades. In reality, consistency lies in disciplined behavior over time - not in avoiding losses altogether. Even the most successful traders experience losing streaks and drawdowns; their edge is in how they manage these inevitable setbacks.
Cognitive Biases and Trading Psychology
Human behavior under uncertainty is riddled with cognitive biases, such as:
-
Gambler’s Fallacy: Believing a winning trade is "due" after a losing streak.
-
Hot-Hand Fallacy: Assuming a winning streak will continue indefinitely.
These mental traps influence risk-taking and decision-making, often leading to compounding errors. Effective risk management counteracts such biases by providing a framework for rational decision-making, even in emotionally charged scenarios.
Tools and Techniques for Risk Management
Stop-Loss Strategies
A stop-loss defines the point at which a trade is invalidated. While it seems straightforward, there are several advanced stop-loss methods:
-
Technical Stops: Placed based on market structure, such as support or resistance levels.
-
Volatility Stops: Adjusted dynamically using indicators like ATR (Average True Range).
-
Break-Even Stops: Moving the stop-loss to the entry point once the trade is in profit.
-
Trailing Stops: Gradually moving the stop-loss to lock in profits as the trade progresses.
Take-Profit Strategies
Take-profit targets should reflect both market conditions and risk-reward objectives. Examples include:
-
Fixed R-Multiples: Setting targets as a multiple of the stop size (e.g., 3:1 reward to risk).
-
Dynamic Targets: Adjusting profit targets based on evolving market conditions.
Position Sizing Models
Calculating position size is fundamental to controlling risk. Popular methods include:
-
Fixed Fractional Model: Risking a consistent percentage of account capital per trade.
-
Volatility-Based Sizing: Adjusting position size according to market volatility.
-
Kelly Criterion: A formulaic approach to maximize account growth, though it requires caution due to its reliance on stable historical metrics.
Scaling Techniques
Scaling in or out of trades allows traders to manage capital risk dynamically. For example:
-
Scaling Out: Locking in partial profits reduces the risk of capital loss while retaining the potential for gains.
-
Scaling In: Gradually entering a position can enhance the entry price while controlling initial risk exposure.
Risk Transformation
Risk cannot be eliminated - it can only be transformed. For example:
-
Rolling to Break-Even: Moving stop-losses to the entry point reduces capital risk while increasing positional risk.
-
Double Stop Collapse: Averaging two trades allows one to cancel out the other’s risk if price reverses.
The Power of Compounding and Long-Term Thinking
Compounding is the "eighth wonder of the world." By reinvesting profits rather than withdrawing them, traders unlock exponential account growth over time. However, this requires patience, discipline, and the ability to delay gratification. As Charlie Munger aptly put it, "The first rule of compounding is to never interrupt it unnecessarily."
Key Takeaways
-
Risk is unavoidable but manageable: Focus on controlling losses rather than chasing perfect strategies.
-
Survival first, profits later: Prioritize capital preservation through disciplined risk management.
-
Leverage is a double-edged sword: Use it cautiously to avoid amplifying losses.
-
Behavioral consistency is key: Overcome biases and emotional decision-making by sticking to a pre-defined plan.
-
Diversify your risk tools: Use a combination of stop-losses, position sizing, and scaling techniques for optimal management.
-
Compounding builds wealth: Reinvest profits for exponential growth, resisting the urge to withdraw prematurely.
-
Adopt a long-term perspective: Sustainable trading beats short-term intensity in the marathon of the financial markets.
Conclusion
Risk management is not just a supplementary skill - it’s the foundation of long-term success as a trader. By integrating technical strategies, emotional discipline, and risk controls, traders can navigate market volatility with confidence and resilience. Remember, trading is not a sprint but a marathon, and the traders who win are those who focus on survival and sustainability. Embrace the principles outlined here, and you’ll be well-equipped to thrive in the ever-changing landscape of stocks and crypto trading.
Source: "The ULTIMATE Guide to Risk Management" - Fractal Flow - Pro Trading Strategies, YouTube, Aug 29, 2025 - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qN0-ltRAcV4