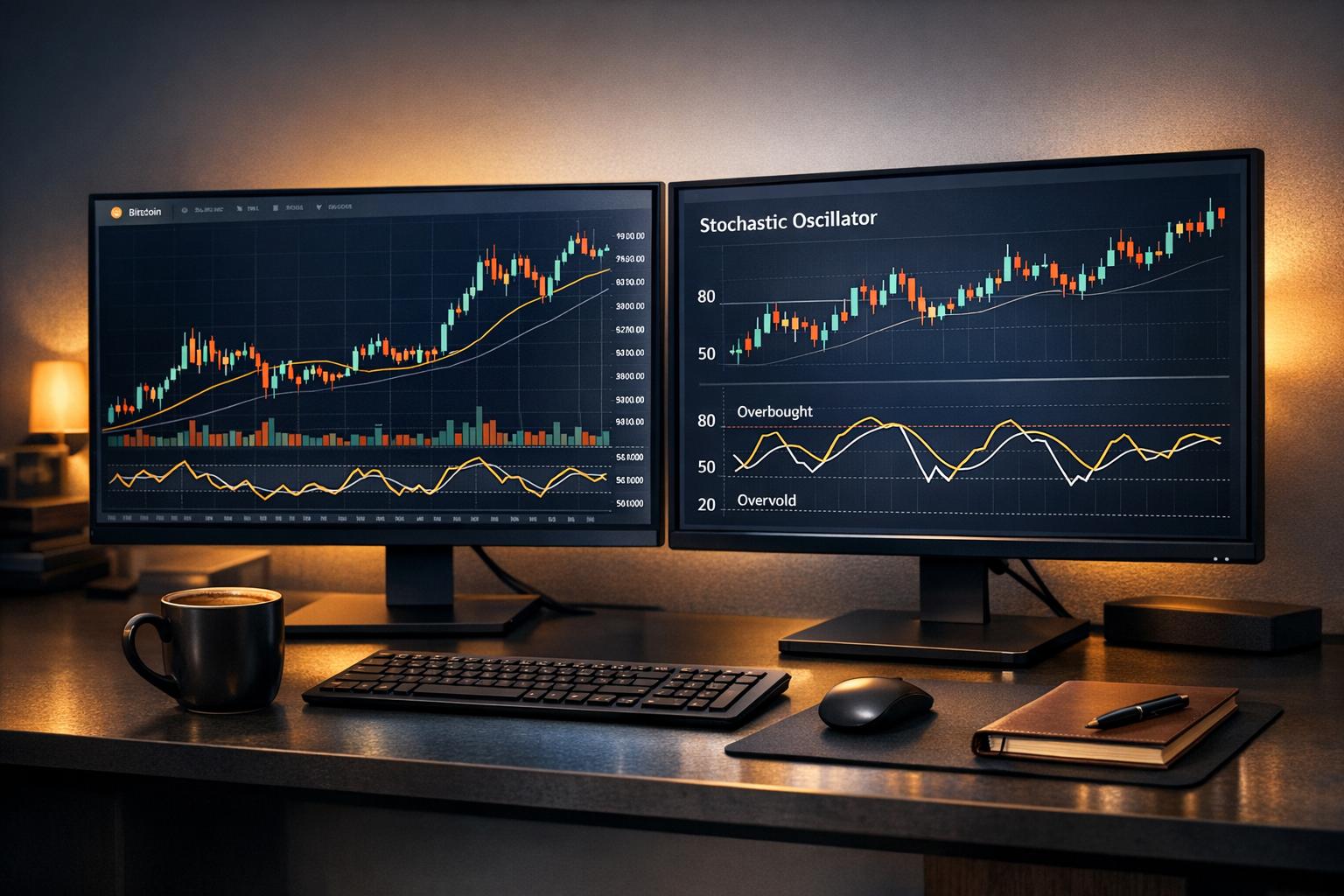
The stochastic oscillator is a popular momentum indicator used in crypto trading to identify potential price reversals. It compares a cryptocurrency's closing price to its price range over a specific period, typically 14 periods, and operates on a scale from 0 to 100. Key features include:
- Overbought (above 80): Indicates a potential pullback.
- Oversold (below 20): Suggests a possible rebound.
- %K Line: Fast-moving line showing the current value.
- %D Line: A 3-period moving average of %K, acting as a signal line.
Traders use the oscillator to spot overbought/oversold conditions, crossovers between %K and %D, and divergence patterns, which can signal momentum shifts. While effective in range-bound markets, it may produce false signals in strong trends or choppy conditions. Tools like StockioAI automate analysis and provide real-time trading signals, helping traders refine their strategies.
Key takeaway: The stochastic oscillator is most useful when combined with other indicators and risk management strategies. Adjusting settings based on trading style and market conditions can improve accuracy.
The Basics of Stochastics Oscillator Trading Explained Simply
Before applying this oscillator, it is essential to analyze crypto trends to ensure you are trading in the direction of the broader market.
How the Stochastic Oscillator is Calculated

Grasping the math behind the stochastic oscillator helps explain why it’s so effective at identifying momentum shifts in crypto trading.
The %K and %D Lines Explained
The %K line serves as the core of the stochastic oscillator. It calculates where the current closing price sits within the recent high-low range. The formula is straightforward:
(Current Close – Lowest Low) / (Highest High – Lowest Low) × 100.
A value of 100 means the price closed at the very top of its range, while a value of 0 indicates it closed at the very bottom.
The %D line, on the other hand, is a 3-period simple moving average of %K. This smoothing process helps cut through short-term fluctuations, making trends easier to spot. Traders often look for crossovers between these two lines: when %K rises above %D, it can signal growing bullish momentum, while %K crossing below %D may hint at bearish pressure. Many view the %D line as a more reliable indicator for trading decisions.
Overbought and Oversold Levels
The oscillator operates on a scale from 0 to 100, with two key thresholds to watch. Readings above 80 suggest overbought conditions, signaling a potential pullback, while readings below 20 indicate oversold conditions, suggesting the price might be nearing a rebound.
For example, a reading of 80 means the price is at the 80th percentile of its range during the selected period. While these levels can highlight potential entry or exit points, traders often wait for %K to cross %D and move back toward neutral territory before taking action.
Choosing the Right Parameter Settings
The default settings - 14, 3, 3 (14-period look-back with 3-period smoothing) - are well-suited for swing trading and range-bound markets. However, the high volatility of cryptocurrencies often calls for adjustments.
For day traders or scalpers dealing with volatile crypto assets, a shorter setting like 5, 3, 3 delivers quicker signals. The downside? Increased sensitivity can lead to more false positives. If you’re focused on long-term trends, settings like 21, 5, 5 can help filter out short-term noise, though signals may lag slightly. The ideal parameters depend on your crypto trading strategies and the specific asset’s behavior.
| Setting Type | %K Length | %K Smoothing | %D Smoothing | Market Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (Default) | 14 | 3 | 3 | Swing trading and range-bound markets |
| Sensitive (Fast) | 5 | 3 | 3 | Scalping or day trading volatile crypto assets |
| Reliable (Slow) | 21 | 5 | 5 | Long-term trend following; reduces false signals |
This structured calculation forms the foundation for interpreting the oscillator's signals, which will be explored in the following sections.
Reading Stochastic Oscillator Signals
The stochastic oscillator, beyond its calculation, offers traders practical insights through its signals. These signals primarily fall into three categories: overbought/oversold levels, crossovers between the %K and %D lines, and divergence patterns. Each type of signal highlights potential momentum changes, helping traders align their technical analysis with market sentiment and current dynamics.
Using Overbought and Oversold Zones
When the stochastic reading climbs above 80, it signals overbought conditions, often hinting at a possible pullback. Conversely, readings below 20 suggest oversold conditions, which might precede a rebound.
However, in strong trends, the oscillator can remain in these extreme zones for extended periods. For instance, Bitcoin might stay overbought during a sustained bull run or oversold during a prolonged market correction. Instead of acting immediately when the oscillator hits 20, many traders look for confirmation, such as the %K line rising back above 20, signaling a shift in momentum. Similarly, a move below 80 from overbought levels can indicate that selling pressure is gaining strength.
%K and %D Crossovers
Crossovers between the fast-moving %K line and the slower %D line provide another layer of insight into momentum shifts. A bullish crossover occurs when %K crosses above %D, particularly when both lines are in the oversold zone (below 20). This suggests that upward momentum may be building. In contrast, a bearish crossover happens when %K drops below %D, especially in the overbought zone (above 80), signaling a potential loss of upward momentum.
"The intersection of these two lines is considered to be a signal that a reversal may be in the works, as it indicates a large shift in momentum from day to day." - Investopedia [4]
For example, Ethereum has shown instances where a steep drop in %K and %D was followed by a rebound, especially when the crossover occurred in extreme zones. Crossovers in these zones often carry more weight than those in neutral areas. After identifying such signals, traders can further refine their analysis by examining divergence patterns.
Spotting Divergence Patterns
Divergence signals occur when price movement and momentum begin to diverge, often hinting at upcoming reversals. A bullish divergence happens when the price forms a new lower low, but the oscillator makes a higher low, indicating that the bearish momentum is weakening. On the flip side, a bearish divergence occurs when the price reaches a new higher high, while the oscillator creates a lower high, suggesting that bullish momentum may be fading.
"Momentum changes often precede price changes." - George Lane [2]
While divergence patterns can act as early warning signs, relying on them alone isn't advisable. Instead, traders often seek confirmation from other indicators like RSI or MACD or observe price behavior around key support and resistance levels.
| Signal Type | Pattern | Market Indication |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish Divergence | Oscillator makes a higher low while price makes a lower low | Weakening bearish trend; potential upward reversal |
| Bearish Divergence | Oscillator makes a lower high while price makes a higher high | Weakening bullish trend; potential downward reversal |
| Bullish Crossover | %K crosses above %D in oversold zone (<20) | Momentum shifting upward; potential buy signal |
| Bearish Crossover | %K crosses below %D in overbought zone (>80) | Momentum shifting downward; potential sell signal |
Trading Strategies Using the Stochastic Oscillator
The stochastic oscillator is a powerful tool for identifying momentum shifts, and these strategies show how to turn its signals into actionable trading decisions. By interpreting overbought/oversold conditions, crossovers, and divergence patterns, traders can navigate various market scenarios with precision.
Trading Overbought and Oversold Conditions
One effective way to use the stochastic oscillator is by trading based on overbought and oversold signals. The key is to wait for confirmation: a rise above 20 from oversold levels or a drop below 80 from overbought levels. For instance, when %K climbs back above 20, it suggests waning downward momentum, signaling a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, when %K falls below 80, it indicates growing selling pressure, which could be a cue to sell or short.
Take Ethereum (ETH) in early July 2024 as an example. At that time, the %K and %D lines sank to 10.02 and 25.49, respectively, placing ETH deep in oversold territory. Traders observed a bounce off the $2,800 support level and entered long positions around $2,850 once the oscillator confirmed the momentum shift. The exit strategy targeted the overbought zone above 80, similar to a pattern seen from May 20 to May 30, 2024, when ETH stayed overbought for 10 days before pulling back [3].
To improve accuracy, filter trades based on the trend. In a strong uptrend, focus on buy signals when the oscillator exits oversold levels. In a downtrend, prioritize sell signals when the oscillator leaves overbought zones.
Momentum Trading with Crossovers
Crossovers between %K and %D offer precise entry and exit signals. A bullish crossover happens when %K crosses above %D while below 20, signaling potential upward momentum. On the other hand, a bearish crossover - when %K crosses below %D above 80 - indicates weakening momentum and a possible reversal.
Patience is key here. Wait for both lines to return to neutral territory before acting on a crossover. For example, after a bullish crossover below 20, ensure both %K and %D rise above 20 before entering a trade. This approach helps confirm the signal's validity.
To refine crossover strategies, use filters like a long-term moving average. For instance, only consider bullish crossovers when the price is above the 200-day EMA. Pairing stochastic crossovers with other indicators, such as RSI or MACD, adds another layer of confirmation. For example, if the stochastic oscillator shows a bullish crossover while the RSI remains neutral, it strengthens the case for a trade. Additionally, monitoring trading volume alongside crossovers can indicate stronger market conviction [3][9].
Combining crossovers with divergence analysis can provide an even clearer picture of market momentum.
Trading Divergence Signals
Divergence patterns are valuable for spotting early signs of trend exhaustion. Bullish divergence occurs when the price makes a lower low while the oscillator forms a higher low, signaling weakening bearish momentum. In contrast, bearish divergence - where the price makes a higher high but the oscillator shows a lower high - indicates fading bullish strength.
"Stochastics measures the momentum of price. If you visualize a rocket going up in the air – before it can turn down, it must slow down. Momentum always changes direction before price." - George Lane [5]
Before trading divergences, confirm them with other factors like price structure, support/resistance levels, and trading volume. For a more cautious approach, wait for a %K and %D crossover after spotting a divergence pattern before committing to a trade [3][8]. Using higher timeframes, such as daily charts, can help filter out noise often found in volatile intraday markets.
Managing Risk and Understanding Limitations
The stochastic oscillator is a useful tool in crypto trading, but like any technical indicator, it has its flaws. Recognizing its limitations is crucial to avoiding costly mistakes and safeguarding your capital in the often unpredictable crypto market.
Common Limitations and False Signals
One of the biggest challenges with the stochastic oscillator arises during strong trending markets. When prices are trending strongly, the oscillator can remain in overbought or oversold zones for extended periods. This phenomenon, often called "overbought/oversold persistence", can mislead traders into exiting profitable trades too early or entering positions that go against the trend [1][2][4].
"The stochastic oscillator tends to generate false signals in strong trends. In uptrends, the oscillator may show overbought conditions for extended periods, but prices can continue to rise." - Investopedia [2]
Another issue is the oscillator's tendency to produce false signals in choppy, sideways markets. In such conditions, the %K and %D lines frequently cross without leading to meaningful price movements. These "whipsaws" can result in small, repeated losses that eat away at profits [2]. This problem becomes even more pronounced on lower timeframes, like 5-minute or 15-minute charts, where market noise often drowns out actionable signals. Additionally, the oscillator's lagging nature can delay signals, making it harder to act on them in a timely manner [2].
Understanding these limitations underscores the importance of disciplined risk management.
Risk Management Techniques
To navigate these challenges, adopting strong risk management practices is essential:
-
Position sizing and stop-loss placement are key to protecting your capital. Limit your risk to 1-2% of your total trading capital per trade and place stop-losses just beyond the most recent swing point. For instance, if you go long on Solana at $95 after a bullish crossover below 20, and the recent swing low is at $92, set your stop at $91.50. This approach minimizes losses from sudden reversals while allowing your trade some breathing room [10][11][12].
-
Aligning trades with the trend can greatly improve your success rate. Only take buy signals when the price is above the 200-day EMA, and only consider sell signals when it's below [6]. This simple filter helps you avoid trades that go against the prevailing market direction. You can also fine-tune the oscillator's sensitivity to match market conditions - use longer periods like 21-28 for smoother signals in volatile markets, or stick to the standard 14-period setting for a balanced approach [2][7].
Using StockioAI for Better Risk Control
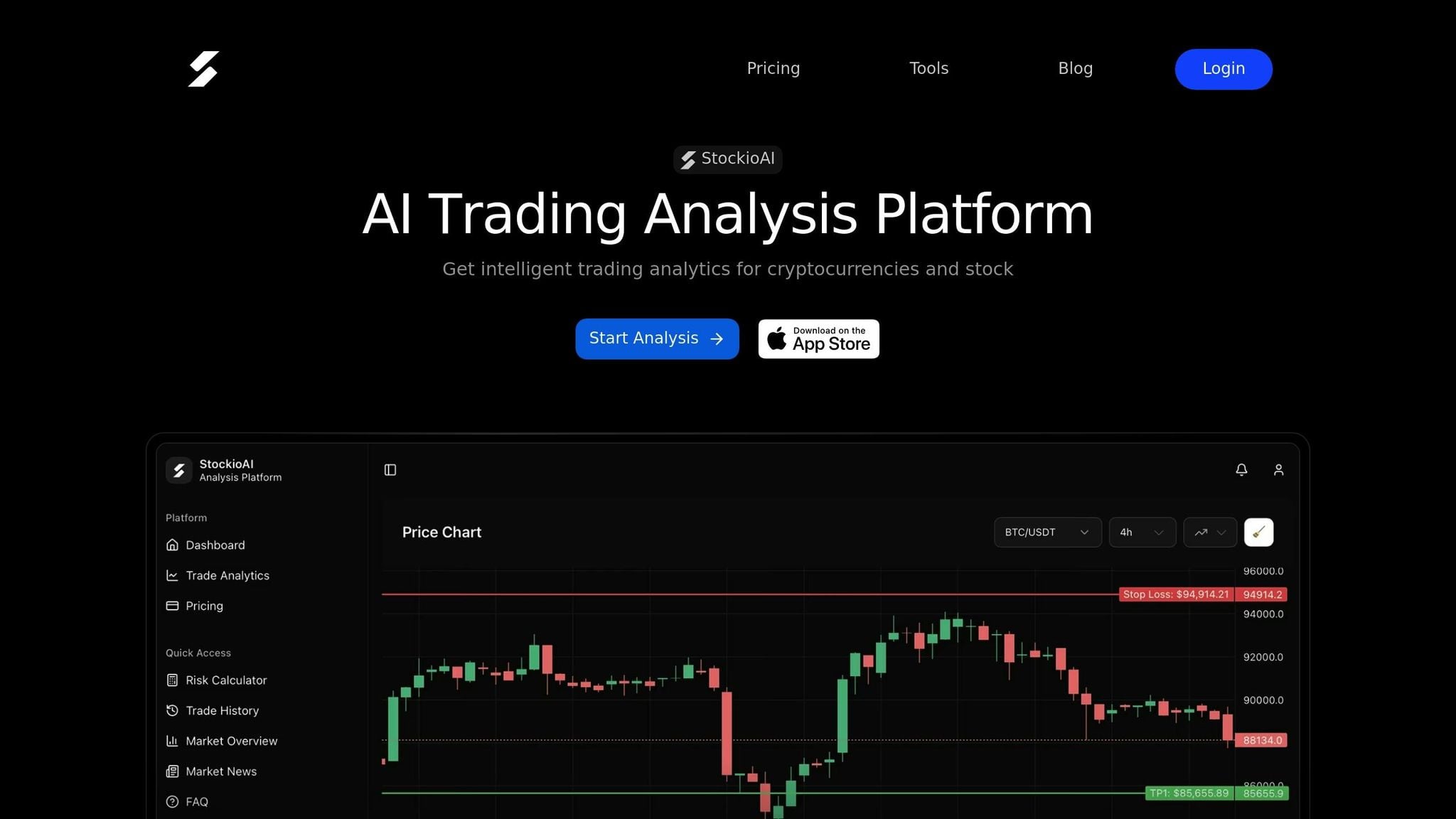
StockioAI takes risk management a step further by incorporating advanced tools for pattern recognition that enhance decision-making. One of its standout features is multi-timeframe analysis, which allows you to align short-term signals on 2-hour or 4-hour charts with the broader trends seen on daily or weekly charts. This helps filter out the noise that often plagues single-timeframe strategies [10][11][6]. For example, it prevents you from acting on a bullish crossover on a 1-hour chart if the daily trend is clearly bearish.
The platform also includes risk calculators that automate position sizing based on your account balance and risk tolerance, removing emotional biases from your trades [10]. Additionally, StockioAI's portfolio tracking tools let you monitor the performance of stochastic-based trades across multiple cryptocurrencies, helping you identify which settings and timeframes yield the best results for your strategy.
StockioAI's confirmation tools further strengthen your trading decisions. By integrating additional indicators - such as the 200 EMA, Average True Range (ATR), or key support and resistance levels - you can create a multi-layered confirmation system [10][6][7]. For instance, if you spot a bullish crossover below 20 but the price is below the 200 EMA and near a strong resistance level, StockioAI can highlight this conflicting trend, helping you avoid a risky trade. This layered approach ensures the stochastic oscillator becomes part of a well-rounded risk management strategy.
Key Takeaways
The stochastic oscillator, introduced by Dr. George Lane, measures an asset's closing price relative to its 14-day price range. It includes two lines: the %K line, representing the current oscillator value, and the %D line, which is a three-day simple moving average of the %K line.
This tool works best when paired with other confirmation methods. A bullish signal might emerge when the %K line crosses above the %D line in oversold territory, while a bearish signal could appear when the %K line drops below the %D line in overbought territory. Divergence between price and momentum can also signal potential reversals.
Keep in mind that extreme readings can linger in strongly trending or choppy markets, leading to false signals. To navigate this, traders often rely on trend filters like a 200-day EMA to align trades with the broader market direction. Understanding these limitations highlights the importance of using additional confirmation tools.
StockioAI enhances stochastic-based strategies by offering multi-timeframe analysis to align short-term signals with long-term trends. Its features - such as automated risk calculators, portfolio tracking, and integrated tools like moving averages and support/resistance levels - provide a well-rounded view of the market, helping traders fine-tune their approaches.
In the crypto world, the 14-period "Slow" stochastic is popular for its balance between responsiveness and noise reduction. However, adjustments can be made - such as using a 5-period for day trading or 21–28 periods for swing trading - to suit different trading styles. Always wait for confirmation from price action or other indicators before committing to a trade. These insights emphasize the importance of combining momentum analysis with solid risk management to refine trading strategies effectively.
FAQs
How does the stochastic oscillator identify momentum changes in cryptocurrency trading?
The stochastic oscillator is a handy tool for traders looking to identify momentum shifts in cryptocurrency markets. It works by comparing the closing price of a cryptocurrency to its recent high-low range. This comparison produces two lines: %K, also known as the fast line, and %D, the slower, smoother line. When the price closes near the recent highs, these lines move upward; when it closes near the lows, they head downward.
Key momentum signals come from %K/%D crossovers or when the oscillator enters extreme zones - above 80 indicates an overbought condition, and below 20 suggests oversold levels. These signals can help traders spot possible trend reversals or confirm the strength of ongoing trends. Tools like StockioAI can monitor these patterns in real time, offering insights to make smarter trading decisions.
What are the ideal stochastic oscillator settings for trading in volatile cryptocurrency markets?
In the fast-moving world of cryptocurrency trading, many traders tweak the stochastic oscillator settings to make it more responsive to rapid price changes. A popular choice is a 5-period %K combined with a 3-period %D smoothing (5,3,3), which reacts more quickly to market shifts. On the other hand, the more traditional 14-period %K with a 3-period %D (14,3,3) remains a trusted option for broader market analysis.
Adjusting these settings to align with your trading strategy and the current market environment can provide sharper insights into potential entry and exit opportunities.
How can traders reduce the risk of false signals when using the stochastic oscillator?
To reduce the chances of being misled by false signals from the stochastic oscillator, traders can rely on additional tools and well-defined risk management strategies. One effective approach is adjusting the oscillator to a slower setting, like 5-3-3, which helps smooth out fluctuations and makes crossovers more dependable. Still, it's always a good idea to confirm these signals with other indicators, such as RSI, moving averages, or patterns in price action, before making a move.
Once a signal checks out, having a plan in place is key. Traders should set clear entry points, stop-loss levels, and profit targets to stay disciplined. For instance, placing a stop-loss just beyond the most recent swing low for long trades - or swing high for short trades - can help limit potential losses. On top of that, controlling position sizes by risking a fixed percentage of account equity, like 1-2%, ensures exposure stays in check.
Platforms like StockioAI make this process easier by offering real-time stochastic signals, automated stop-loss suggestions, and AI-driven analysis of patterns. These tools empower traders to make smarter decisions while keeping false signals to a minimum.